When an unexpected electrical surge hit Sarah’s small business, the LED luminaires she had installed to save on energy costs became a dangerous liability. The lack of proper protection highlighted the importance of understanding IEC protection classes for LED luminaires. These classes are designed to safeguard against electrical hazards, ensuring safety and efficiency in lighting solutions.
IEC protection classes are not just technical jargon but essential for anyone using LED lighting. According to a recent study, improper electrical protection in lighting fixtures is responsible for over 30% of electrical accidents in commercial settings. This statistic underscores the need for thorough knowledge and application of IEC standards in all lighting projects.
This comprehensive guide will explore the different IEC protection classes, their features, and how they can prevent accidents like Sarah’s. Stay with us as we delve into the intricacies of these classifications, providing you with the knowledge to make informed decisions for safer, more reliable LED lighting installations.
Understanding IEC Protection Classes for LED Luminaires
LED technology has dramatically transformed the lighting industry, offering unparalleled energy efficiency and versatility. However, ensuring the safety and functionality of LED luminaires requires a thorough understanding of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) protection classes. These classes are crucial for categorizing the levels of protection against electrical shock provided by different types of luminaires.
Introduction to IEC Protection Classes
Overview of IEC Standards
Founded in 1906, the IEC has been at the forefront of developing global standards for electrical and electronic technologies. The organization has continually evolved its standards to keep pace with technological advancements, ensuring safety and efficiency remain paramount in the design and implementation of electrical products.
IEC standards are globally recognized guidelines for electrical and electronic products’ safety, performance, and compatibility criteria. These standards ensure products meet rigorous safety requirements, thus protecting consumers and environments from potential hazards.
Importance of Protection Classes in LED Luminaires
Protection classes in LED luminaires are essential for determining safety measures to prevent electrical shocks. They guide manufacturers in designing products that mitigate risks, ensuring safe usage across various applications. Understanding these classes helps select the appropriate luminaires for specific environments, enhancing safety and performance.
What Are IEC Protection Classes?
IEC protection classes define the levels of protection an electrical device offers against electrical shock. These classes ensure devices are safe for use by providing guidelines for insulation, grounding, and protective measures.
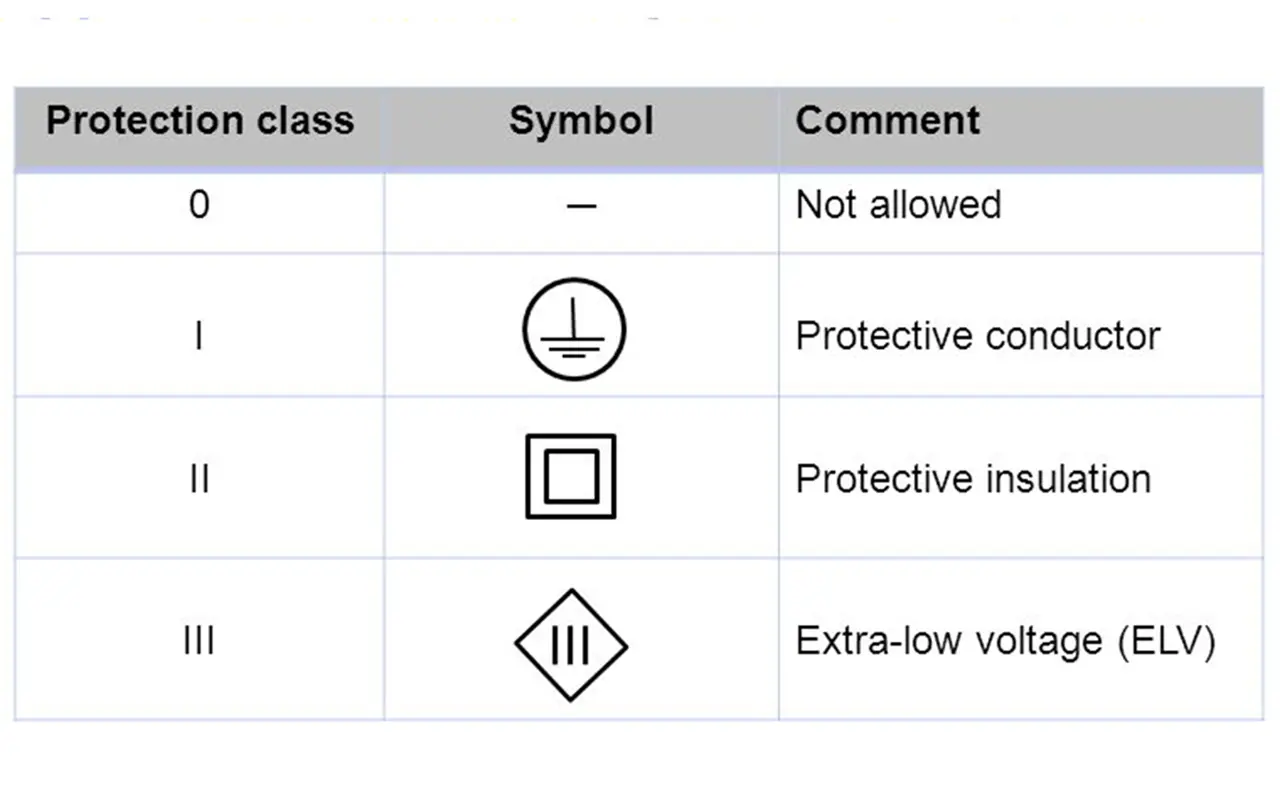
IEC protection classes are categorized based on the insulation systems and grounding connections of electrical devices. The classes range from 0 to III, each offering different levels of protection and suitability for various applications.
Different Types of IEC Protection Classes
IEC Class 0: No Protection
Class 0 devices rely solely on basic insulation, typically provided by the PVC coating on wires. They lack a protective earth (PE) connection, making them highly susceptible to electrical shocks and unsuitable for environments where safety is paramount.
The primary advantage of Class 0 devices is their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. However, their inadequate protection poses significant risks, leading to their prohibition in many regions.
IEC Class 01: Limited Protection
Class 01 devices slightly improve over Class 0 by allowing an earth connection. However, they still pose considerable risks and are rarely used in residential or commercial settings.
While Class 01 provides some level of grounding, its protection still needs to be improved for most applications, rendering it less favorable compared to higher classes.
IEC Class I: Basic Protection
Class I devices incorporate basic insulation along with a grounding connection. They use a three-pin plug with live, neutral, and ground wires, ensuring all metal components are earthed and safe to touch.
Class I devices are widely used due to their enhanced safety features, including fuses and circuit breakers that provide an additional layer of protection. However, they require proper grounding infrastructure, which may only be available in some settings.
IEC Class II: Enhanced Protection
Class II devices, known as double-insulated appliances, feature two layers of insulation, eliminating the need for grounding. These devices prevent electrical shocks even if one insulation layer fails.
Class II devices are highly versatile and safe, suitable for various applications where grounding is not feasible. Their primary drawback is the complexity and cost associated with the additional insulation.
Class II luminaires must have a minimum aperture of 3 mm and a creepage distance of 5 mm. They should be designed to prevent direct contact with electrical components, ensuring maximum safety.
IEC Class III: Extra Low Voltage Protection
Class III devices operate on Separated Extra-low Voltage (SELV), typically 50 V AC or lower. This low voltage significantly reduces the risk of electrical shock, making these devices ideal for high-risk environments.
The primary advantage of Class III devices is their inherent safety due to the low operating voltage. However, they may require specialized transformers and may only be suitable for some applications.
Class III devices often utilize isolating transformers, which separate the primary and secondary windings to prevent direct electrical contact. This isolation ensures that the devices remain safe even if the transformer fails.
The Importance of IEC Certification
Why IEC Certification Matters
IEC certification is a cornerstone of safety and reliability in electrical devices. This certification is not merely a bureaucratic hurdle but a comprehensive assessment that ensures products adhere to rigorous international safety standards. IEC certification on an electrical product signifies that it has undergone extensive testing and evaluation to confirm its safety, reliability, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
For consumers, IEC certification instills confidence. When a product bears this certification, users can be assured that it meets the highest quality and safety standards. This is particularly critical for LED luminaires, where improper design or faulty components can lead to electrical shocks, fires, or other hazards. IEC certification minimizes these risks by enforcing strict guidelines on insulation, grounding, and other protective measures.
Moreover, IEC certification facilitates international trade by ensuring that products meet global safety standards. This uniformity helps manufacturers sell their products in multiple markets without additional testing, thus simplifying the regulatory landscape and reducing costs. It also enhances the reputation of manufacturers, as adherence to IEC standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and safety.
The Certification Process Explained
The IEC certification process is thorough and multifaceted, designed to evaluate electrical devices rigorously against predefined standards. This process begins with submitting product samples to accredited testing laboratories, where a series of tests are conducted to assess various safety and performance parameters.
Key aspects of the certification process include:
- Insulation Testing: This test ensures the electrical insulation is robust enough to prevent accidental contact with live parts. It involves applying high voltage to the insulation material and checking for breakdowns.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding is essential to direct any fault currents away from users safely. The certification process evaluates the effectiveness of grounding mechanisms and ensures all conductive parts are adequately bonded.
- Thermal Testing: This assesses the ability of the luminaire to operate within safe temperature ranges. It includes testing the heat dissipation mechanisms to prevent overheating, which could lead to fire hazards.
- Ingress Protection (IP) Testing: This evaluates the device’s resistance to dust and water ingress, ensuring it can operate safely in various environmental conditions.
- Mechanical Testing: This involves checking the structural integrity of the device to withstand physical impacts and vibrations, which is crucial for ensuring long-term durability and safety.
- Performance Testing: These tests ensure that the luminaire performs as expected regarding light output, efficiency, and lifespan.
Once the product passes these tests, the results are reviewed by an independent certification body. If all criteria are met, the product is awarded the IEC certification, which it can then display to signify compliance with international standards.
The certification process continues after initial approval. Periodic audits and re-testing are conducted to ensure continued compliance, especially when there are changes in design or manufacturing processes. This ongoing scrutiny helps maintain high safety and performance standards, ensuring certified products remain reliable throughout their lifecycle.
Benefits of IEC Protection Classes in LED Luminaires
Ensuring Safety and Compliance
IEC protection classes ensure that LED luminaires adhere to stringent safety standards, minimizing the risk of electrical shocks and other hazards. These regulations are designed to protect users and maintain high safety levels in various environments.
Compliance with IEC standards enhances the credibility of manufacturers, instilling confidence in consumers and regulatory bodies. It also facilitates international trade by ensuring that products meet global safety requirements.
Enhancing Durability and Performance
IEC protection classes help safeguard LED luminaires from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and temperature variations. This protection extends the lifespan of the devices and ensures consistent performance.
Devices that comply with IEC standards are typically more durable and require less maintenance. These luminaires’ robust design and high-quality materials contribute to their longevity and reliability.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
IEC-certified LED luminaires are designed for optimal energy efficiency, reducing power consumption and lowering electricity bills. This efficiency is achieved through advanced technologies and superior design.
The cost savings associated with reduced energy consumption and lower maintenance requirements make IEC-certified luminaires a cost-effective choice in the long run. These financial benefits and enhanced safety make them an attractive option for various applications.
Environmental Considerations
IEC Protection Classes and Environmental Factors
IEC protection classes play a pivotal role in safeguarding LED luminaires from environmental factors that could compromise their performance and safety. These standards ensure that LED devices are robust enough to withstand different operating conditions, enhancing their longevity and reliability.
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, and exposure to chemicals can significantly impact the functionality of LED luminaires. For instance, high temperatures can lead to thermal stress, which may degrade the performance of LEDs or even cause them to fail prematurely. Similarly, high humidity levels can cause condensation and corrosion, affecting the luminaires’ electrical and structural integrity.
The IEC standards categorize protection levels to address these specific challenges. For example, IEC 60529 outlines the degrees of protection provided by enclosures against intrusion (IP ratings), which includes protection against dust and water ingress. For instance, an LED luminaire with an IP65 rating is dust-tight and protected against water jets from any direction, making it suitable for outdoor applications where it may be exposed to rain and dust.
Protecting LED Luminaires from Harsh Conditions
To ensure the longevity and reliable performance of LED luminaires, it is crucial to adhere to the appropriate IEC protection classes tailored to the environmental conditions they will face. Harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures, high humidity, and corrosive environments, demand specific protective measures.
- Extreme Temperatures: LED luminaires operating in environments with extreme temperatures require effective thermal management systems. This includes using heat sinks and thermally conductive materials that dissipate heat away from the LED chips, preventing thermal stress and ensuring optimal performance. The IEC 60598-1 standard specifies thermal endurance tests that luminaires must pass to ensure they can operate safely within specified temperature ranges.
- High Humidity and Condensation: High humidity levels and condensation can lead to short circuits and corrosion of internal components. LED luminaires should be designed with adequate sealing and protective coatings to combat this. IEC standards such as IEC 60598-2-22 provide guidelines on constructing and testing luminaires to ensure they are resistant to moisture ingress.
- Corrosive Environments: In environments where luminaires are exposed to corrosive substances, such as industrial facilities or coastal areas, it is essential to use materials resistant to corrosion. This includes stainless steel, anodized aluminum, or specially coated metals that can withstand harsh chemical exposure. The IEC 60068-2-60 standard details methods for testing the resistance of materials to corrosive atmospheres, ensuring that luminaires maintain their integrity and performance over time.
- Dust and Particulate Matter: Dust and particulate matter can infiltrate luminaires and affect their performance. An appropriate IP rating, such as IP6X, ensures the luminaire is completely protected against dust ingress. This is particularly important for outdoor and industrial applications where dust is prevalent.
Selecting the Right IEC Protection Class for Your Needs
Assessing Your Application Requirements
Environmental Considerations
When selecting an IEC protection class, it is essential to consider the environmental conditions in which the luminaire will operate. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to elements play a critical role in determining the appropriate protection class.
Usage Scenarios
Different applications require different levels of protection. For instance, outdoor lighting may require Class III luminaires due to their exposure to weather conditions, while indoor lighting in a controlled environment may only need Class I or II.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Overlooking Specific Needs
One common mistake is failing to assess the application’s specific needs, leading to the selection of an inappropriate protection class. Evaluating all relevant factors to ensure optimal safety and performance is crucial.
Misunderstanding Protection Levels
Another mistake is misunderstanding the protection levels provided by each Class. Clear knowledge of the distinctions between classes 0, I, II, and III is necessary to make informed decisions.
Ensuring Safety and Preventing Hazards
How to Protect Yourself from Getting Electrocuted
Protecting yourself from electrical hazards is paramount when dealing with LED luminaires or any other electrical installations. Here are key steps to ensure your safety:
- Changing the Bulb: Always turn off the power before changing a bulb. Ensure that the fixture is not live to avoid electrical shock. Use a voltmeter to check for any residual voltage.
- Outdated Outlets: Replace outdated or damaged outlets that lack proper grounding. Two-prong outlets without grounding pose significant risks and should be upgraded to meet current safety standards.
- Electricity Touching Water: Never handle electrical fixtures with wet hands or near water. Water is a conductor of electricity and can cause severe shocks. Ensure the area is dry before working on any electrical installation.
- Mishandling Electricity: Always follow safety protocols when handling electrical installations. Use personal protective equipment such as insulating gloves and aprons, and seek professional assistance.
Why Do LEDs Explode?
- Electrical Stresses: LEDs can explode due to electrical overstress (EOS) caused by voltage fluctuations or faulty capacitors. Always use high-quality components to mitigate this risk.
- Thermal Stresses: Inadequate heat dissipation can lead to thermal stress, causing LEDs to overheat and explode. Ensure proper heat sinks and ventilation are in place to prevent thermal buildup.
- LEDs Exploding in Enclosed Fixtures: Enclosed fixtures can trap heat, leading to thermal stress and potential explosions. Use LEDs rated for enclosed fixtures to avoid this issue.
- Loose Socket Connections: Loose connections can cause sparking and heat buildup, leading to explosions. Ensure all connections are secure and tight to prevent this hazard.
- Lack of Insulation: Poor insulation can result in electrical faults and explosions. Always use LEDs with adequate insulation to ensure safety.
- Mismatched Voltages: Using LEDs with incorrect voltage ratings can cause them to overheat and explode. Check the voltage requirements before installation.
The Cause of Fire
Overloaded Circuits: Overloading electrical circuits can cause overheating and fire. Ensure circuits are not overloaded and are designed to handle the load.
Poor Quality Components: Low-quality components can fail and cause fires. Always use high-quality, certified components to ensure safety.
Is Dimming LEDs Dangerous?
Circuit Overload: Dimming LEDs can cause circuit overload if not designed correctly. Use compatible dimmers to avoid this issue.
Grid Problem: Fluctuations in the power grid can affect the performance of dimmable LEDs. Ensure the electrical system is stable and well-maintained.
Lamp Life Has Exceeded: Old and worn-out LEDs can malfunction and pose safety risks. Replace aging LEDs to maintain safety and performance.
Real-world Examples and Case Studies
Successful Implementations of IEC Class I
Class I luminaires are a staple in residential and commercial applications thanks to their reliable safety features and robust construction. These luminaires utilize a grounding wire to provide additional protection against electrical shocks, making them ideal for environments where safety is paramount.
- Residential Applications
In residential settings, Class I luminaires are commonly found in areas such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor spaces where moisture and humidity are prevalent. The grounding mechanism in these luminaires helps mitigate the risk of electrical hazards by ensuring that any stray electrical currents are safely directed to the ground.
One notable example of successful implementation is using Class I outdoor LED floodlights. These lights are often installed in gardens, driveways, and building exteriors, where they are exposed to various environmental factors. The grounding wire provides a crucial safety measure, protecting users from potential electrical faults due to moisture ingress or physical damage to the luminaire.
- Commercial Applications
In commercial settings, Class I luminaires are extensively used in offices, retail spaces, and industrial environments. For instance, Class I LED panel lights are preferred in an office building due to their enhanced safety features and compliance with stringent electrical safety regulations. These lights provide excellent illumination and ensure that the workplace remains safe from electrical hazards.
In industrial environments, where heavy machinery and equipment are in constant operation, Class I high-bay LED lights are widespread. These luminaires are designed to withstand harsh conditions and provide reliable lighting while minimizing the risk of electrical accidents through effective grounding.
Successful Implementations of IEC Class II
Class II luminaires are designed with double or reinforced insulation, eliminating the need for grounding and providing enhanced protection against electrical shocks. This makes them particularly suitable for applications where grounding may not be feasible or necessary.
- Consumer Electronics
Class II luminaires are prevalent in consumer electronics due to their ease of installation and safety features. For example, LED desk lamps and portable reading lights often fall under the Class II category. These devices are designed with multiple layers of insulation to ensure user safety, even in the event of internal faults.
The widespread adoption of Class II luminaires in consumer electronics is driven by their ability to provide high levels of safety without the need for complex grounding systems. This makes them ideal for use in homes, schools, and offices where portability and ease of use are essential.
- Household Appliances
Class II luminaires are also commonly found in appliances such as LED televisions, kitchen appliances, and bathroom fixtures. The double insulation design ensures that these devices remain safe, even in environments with moisture and humidity.
For instance, LED bathroom mirrors with integrated lighting are a popular application of Class II luminaires. These mirrors provide excellent illumination while protecting users from electrical shocks, thanks to the reinforced insulation.
Successful Implementations of IEC Class III
Class III luminaires use Separated Extra-low Voltage (SELV) systems, which provide maximum safety by operating at voltages below 50V AC. This makes them ideal for high-risk environments where electrical safety is paramount.
- Medical Applications
Class III luminaires are essential in medical settings due to their inherent safety features. For example, surgical lights and examination lamps often utilize SELV systems to ensure that there is no risk of electrical shock to patients and medical staff. These luminaires provide the necessary illumination for critical medical procedures while maintaining the highest electrical safety standards.
- Industrial Applications
In industrial environments, Class III luminaires are used in hazardous areas where the risk of electrical shock needs to be minimized. For instance, LED strip lights used in mining operations or chemical plants often operate on SELV systems to ensure worker safety. These lights provide reliable illumination in challenging conditions while adhering to stringent safety regulations.
Future Trends in IEC Protection for LED Luminaires
Emerging Technologies
The field of LED lighting is continuously evolving, with technological advancements driving new trends and innovations. One of the most significant emerging trends is integrating smart lighting systems. These systems leverage the Internet of Things (IoT) to offer remote control, automation, and energy management features. Smart LED luminaires can be controlled via smartphones or voice assistants, allowing users to adjust lighting levels, color temperatures, and schedules easily.
Another promising technology is improved heat dissipation mechanisms. As LEDs become more powerful and compact, managing heat becomes crucial to maintain performance and longevity. Innovations such as advanced thermal management materials, enhanced heat sinks, and active cooling systems are being developed to address these challenges. These technologies ensure that LED luminaires operate efficiently while extending their lifespan.
Evolving Standards and Regulations
As LED technology advances, so do the standards and regulations that govern their safety and performance. The IEC regularly updates its standards to reflect new developments and address emerging challenges. Staying informed about these changes is essential for manufacturers, installers, and users to ensure compliance and maintain safety.
For instance, new regulations may focus on electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), energy efficiency, and environmental impact. These evolving standards aim to enhance LED luminaires’ overall safety and sustainability, ensuring they meet the highest quality benchmarks.
Moreover, with the growing emphasis on sustainability, future standards may incorporate guidelines for the recyclability and disposal of LED luminaires. This will not only help in reducing electronic waste but also promote the development of eco-friendly lighting solutions.
FAQs
Q: What are IEC protection classes, and why are they important for LED luminaires?
A: IEC protection classes categorize the levels of electrical shock protection provided by electrical devices. These classes are crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of LED luminaires and guiding manufacturers in designing products that meet international safety standards.
Q: How are IEC protection classes categorized?
A: IEC protection classes are categorized based on the insulation systems and grounding connections of electrical devices. The classes range from 0 to III, each offering different levels of protection, with Class III providing the highest level of safety through extra-low voltage systems.
Q: What is the difference between Class I and II LED luminaires?
A: Class I LED luminaires have basic insulation and require a grounding connection for safety. Class II luminaires, however, feature double or reinforced insulation, eliminating the need for grounding and providing enhanced protection against electrical shocks.
Q: Why are Class III luminaires considered the safest?
A: Class III luminaires operate on Separated Extra-low Voltage (SELV), typically below 50 V AC. This low voltage significantly reduces the risk of electrical shock, making these luminaires ideal for high-risk environments such as medical facilities and outdoor applications.
Q: What are the benefits of using IEC-certified LED luminaires?
A: IEC-certified LED luminaires ensure compliance with international safety standards, enhancing product reliability, reducing the risk of electrical hazards, and often providing energy efficiency and cost savings due to their high-quality design and materials.
Q: Can Class 0 devices be used in residential or commercial settings?
A: Class 0 devices are not recommended for residential or commercial settings due to their inadequate protection against electrical shocks. Many regions have prohibited their use because they rely solely on basic insulation without grounding.
Q: What precautions should be taken when changing an LED bulb to avoid electrical shock?
A: Always turn off the power at the switch and, if possible, at the circuit breaker before changing an LED bulb. Use a voltmeter to ensure no residual voltage, and handle the bulb with dry hands to prevent electrical shock.
Q: Why do LEDs sometimes explode, and how can this be prevented?
A: LEDs can explode due to electrical overstress (EOS) from voltage fluctuations or thermal stress from inadequate heat dissipation. Prevent this by using high-quality LEDs with proper heat sinks and ensuring they are rated for enclosed fixtures if necessary.
Q: Are dimmable LEDs dangerous, and what should be considered when using them?
A: Dimmable LEDs are not inherently dangerous; improper use can lead to circuit overload. Ensure compatibility between the LEDs and dimmer switches and monitor for any signs of flickering or overheating.
Q: How do environmental factors affect the performance of LED luminaires?
A: Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to elements can impact the performance and lifespan of LED luminaires. Choosing the appropriate IEC protection class for the specific environment ensures reliable operation and longevity of the luminaires.
Fazit
Understanding IEC protection classes is essential for ensuring the safety and performance of LED luminaires. Each Class offers different levels of protection that are suitable for various applications. By selecting the right protection class, you can ensure optimal safety, compliance, and performance in your lighting solutions.
Unitop stands out as one of China’s leading LED-Leuchtbänder und LED-Neon-Flex manufacturers for those seeking the highest quality LED products. Our expertise and dedication to excellence ensure that we meet the highest safety and performance standards. If you have further questions or specific requirements, please do not hesitate to Kontaktieren Sie uns. We are here to provide you with professional guidance and top-notch LED solutions.

Tom ist jetzt der Verkaufsleiter von Unitop (China) Co., Limited. Er war in der LED-Beleuchtung Industrie seit 2005. Er ist Experte für Vertrieb und Marketing sowie für Fabrikmanagement. Er mag Bodybuilding und ist außerdem ein verrückter Apple-Fan! Er ist ein fleißiger Kerl und liebt es, neue Dinge zu lernen und auszuprobieren.
E-Mail: tom@unitopledstrip.com WhatsApp: +86-18680307140







Hinterlasse einen Kommentar
An der Diskussion beteiligen?Hinterlasse uns deinen Kommentar!