Industrial lighting creates a safe, efficient, and productive work environment. Proper lighting can significantly impact operational performance, worker safety, and energy consumption. Whether you manage a warehouse, factory, or any large-scale industrial facility, understanding the essentials of industrial lighting can help you make informed decisions that enhance functionality and cost-effectiveness.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various types of industrial lighting, from energy-efficient LEDs to specialized explosion-proof fixtures, and delve into the key considerations for designing an optimal lighting system. We’ll also discuss the latest technological advancements, including smart lighting systems and human-centric lighting (HCL), revolutionizing industrial spaces. This guide provides valuable insights for facility managers, business owners, and anyone looking to improve their industrial lighting setup.
Ready to transform your industrial lighting setup? Let’s dive right in and explore the essentials that will illuminate your path to success. Whether you want to upgrade to LED strip lights, optimize energy efficiency, or implement advanced lighting controls, this guide covers you.
Types of Industrial Lighting
LED Lighting: The Modern Solution
Benefits of LED Lighting
LED lighting has revolutionized industrial lighting with its energy efficiency and longevity. LEDs consume significantly less power than traditional lighting, leading to substantial cost savings. Moreover, they have an impressive lifespan of up to 50,000 hours, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance efforts.
The benefits of LED lighting extend beyond just energy savings. LEDs offer superior light quality, with higher Color Rendering Index (CRI) values that ensure accurate color representation. This is critical in environments where precision is essential, such as in manufacturing and quality control areas. LEDs also provide instant illumination without the warm-up time required by other lighting types, ensuring that workspaces are immediately well-lit when needed.
Applications of LED Lighting in Industry
LEDs are highly versatile and can be used in various industrial applications. From high bay lighting in warehouses to task lighting in assembly lines, LEDs provide bright, clear illumination that enhances visibility and safety. They are also ideal for outdoor security lighting and emergency lighting systems.
In warehouses and distribution centers, high-bay LED lights are particularly effective. These fixtures can be mounted at great heights and provide powerful, even illumination across large areas. This is essential for inventory management and order-picking tasks, where clear visibility is crucial.
LEDs can be used in various forms, such as under-cabinet, adjustable arms, and machine lights for task lighting. These provide focused illumination that helps workers perform detailed tasks with greater accuracy. In areas where hazardous materials are handled, explosion-proof LED lights are available to ensure safety without compromising lighting quality.
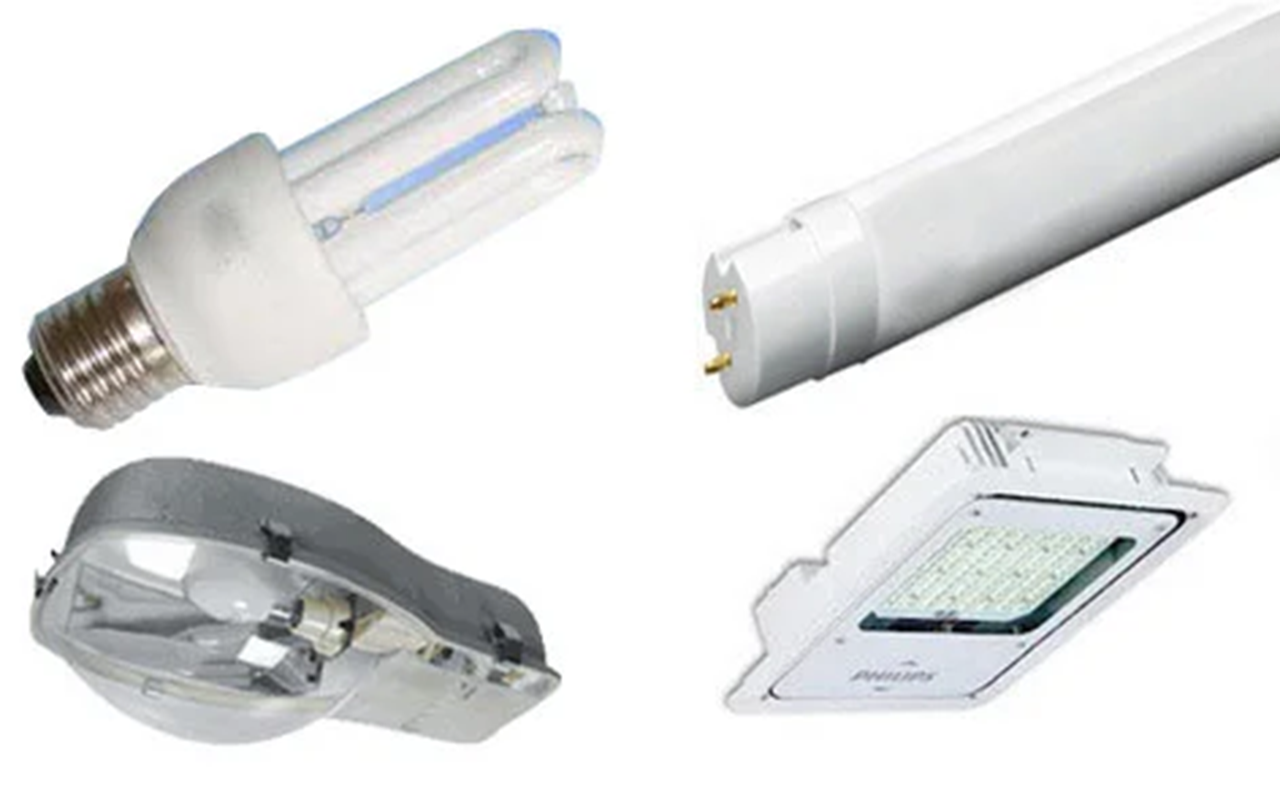
Fluorescent Lighting: Cost-Effective and Efficient
Advantages of Fluorescent Lighting
Fluorescent lights are renowned for their cost-effectiveness and efficiency, making them a go-to option in many industrial settings. These lights emit a bright, uniform light that ensures excellent visibility across large areas, a critical factor in environments where precision and safety are paramount.
One of the primary advantages of fluorescent lighting is its energy efficiency. Fluorescent bulbs consume significantly less energy than incandescent bulbs, translating into substantial cost savings on electricity bills over time. This efficiency makes them an economical choice for businesses looking to reduce operating expenses without compromising lighting quality.
Moreover, fluorescent lights have a longer lifespan than incandescent bulbs, typically lasting between 7,000 to 15,000 hours. This extended lifespan means fewer replacements, which reduces maintenance costs and downtime associated with changing bulbs. The lower heat emission of fluorescent lights also contributes to a cooler working environment, further enhancing comfort and productivity in industrial settings.
Another benefit is the availability of various configurations, such as tube lights and compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs), allowing for flexibility in design and application. Fluorescent lighting is also available in different color temperatures, which can be selected based on the specific needs of the workspace. For example, cool white light (4000K to 5000K) enhances concentration and visibility in task-oriented areas.
Ideal Uses in Industrial Settings
Fluorescent lights suit wide areas such as offices, warehouses, and manufacturing plants. Their ability to provide consistent, flicker-free illumination over large spaces makes them indispensable in environments where clear visibility is essential for safety and efficiency.
In warehouses, fluorescent lighting is often used to illuminate aisles and storage areas, ensuring workers can easily locate and identify items. The uniform light distribution helps reduce shadows and dark spots, which can pose safety risks and slow down operations.
Manufacturing plants also benefit from the bright, even light fluorescent fixtures provide. These lights are typically installed in production lines, assembly areas, and inspection zones, where precise visibility is crucial for maintaining quality control and preventing errors. The energy efficiency and longevity of fluorescent lights make them an economical choice for operating around-the-clock facilities.
HID Lighting: High Intensity for Large Areas
Pros and Cons of HID Lighting
High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lighting is known for its high brightness and is ideal for large spaces that require intense illumination. HID lights include metal halide, high-pressure sodium, and mercury vapor lamps, each with distinct characteristics and applications.
One of the main advantages of HID lighting is its ability to produce very bright light, making it suitable for large, open spaces. HID lights have a high lumen output, covering extensive areas with fewer fixtures. This makes them cost-effective for initial installations in vast industrial settings.
However, HID lighting comes with several drawbacks. One significant disadvantage is its energy consumption. HID lights use more power than LEDs, leading to higher electricity bills. Additionally, HID lamps have a shorter lifespan, typically ranging from 6,000 to 24,000 hours, depending on the type. This shorter lifespan results in more frequent replacements and higher maintenance costs.
Another limitation is the warm-up time required for HID lamps to reach full brightness. This delay can be inconvenient in environments where immediate illumination is necessary. Furthermore, HID lights can produce glare and uneven distribution, affecting visibility and safety in certain areas.
Best Applications for HID Lighting
HID lights are best used in expansive areas such as sports arenas, parking lots, and large warehouses where high-intensity lighting is needed. They provide powerful illumination that covers large spaces effectively.
In sports arenas, HID lights ensure that the entire field or court is evenly lit, providing clear visibility for players and spectators. The high brightness and wide coverage make them ideal for large-scale events and facilities.
Parking lots benefit from the intense illumination provided by HID lights, which enhances safety by improving visibility for drivers and pedestrians. The bright light helps deter criminal activity and reduces the risk of accidents in these outdoor spaces.
For industrial applications, HID lights are commonly used in high bay settings, where they are mounted at great heights to illuminate large areas such as warehouses and distribution centers. The powerful light output ensures that these vast spaces are adequately lit, facilitating efficient operations and enhancing safety.
Incandescent Lighting: Traditional but Obsolete
Disadvantages of Incandescent Lighting
Incandescent lights are less energy-efficient and have a shorter lifespan than other lighting options. They emit a warm light but consume much power and generate more heat, making them less suitable for industrial use.
The operation of incandescent bulbs involves heating a filament until it glows, which is inefficient. Much of the energy consumed by incandescent bulbs is wasted as heat rather than being converted into visible light. This inefficiency translates into higher energy costs, making incandescent bulbs a less economical choice for industrial applications where lights are used extensively.
Additionally, the lifespan of incandescent bulbs is relatively short, typically around 1,000 to 2,000 hours. This means frequent replacements are needed, increasing maintenance costs and operational disruptions. The high heat output of incandescent bulbs can create a less comfortable working environment and necessitate additional cooling measures, further driving up energy costs.
Where Incandescent Lighting is Still Used
Incandescent lighting is mostly phased out in industrial settings but may still be found in some older facilities or specific applications where warm light is preferred for aesthetic reasons.
Incandescent lights might still create a warm, inviting atmosphere in certain hospitality or retail environments. Their warm color temperature is often associated with comfort and coziness, making them suitable for restaurants, cafes, and boutique shops. These settings benefit from the ambiance created by incandescent lighting despite its inefficiency.
Halogen Lighting: Bright and Clear
Benefits of Halogen Lighting
Halogen lights provide bright, clear illumination and have better energy efficiency than incandescent lights. They are known for their excellent color rendering, making them suitable for tasks requiring precise visual accuracy.
Halogen bulbs are a type of incandescent light that contains a small amount of halogen gas, which helps to increase their efficiency and lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. They produce a bright, white light that resembles natural daylight, enhancing visibility and reducing eye strain. Halogen lights also have a higher color temperature and better color rendering capabilities, making them ideal for detailed work.
Another benefit of halogen lighting is its ability to operate at higher temperatures than standard incandescent bulbs, resulting in a higher light output. This makes halogen bulbs more efficient in terms of lumens per watt, providing more light for the same amount of energy consumed.
Suitable Industrial Uses
Halogen lighting is ideal for task lighting in inspection areas, workshops, and places where accurate color representation is crucial. They are also used in display lighting and other applications where high-quality light is needed.
In industrial settings, halogen lights are often used in inspection stations, where precise visual tasks are performed. Their bright, clear light ensures workers can see fine details, which is essential for quality control and accurate assembly. Halogen lights are also used in workshops and laboratories, where machining, painting, and testing require high-quality illumination.
Additionally, halogen lights are popular in display lighting for retail and museum environments, where accurate color representation is important for showcasing products and exhibits. Their bright, white light enhances the appearance of objects, making them more attractive and easier to inspect.
Explosion-Proof Lighting: Safety in Hazardous Environments
Features of Explosion-Proof Lighting
Explosion-proof lighting is designed to operate safely in hazardous environments where flammable gases or combustible dust are present. These lights are constructed with durable, heat-resistant materials and often include safety features like reinforced glass and emergency shut-off switches.
The primary feature of explosion-proof lighting is its ability to contain sparks or flames within the fixture, preventing them from igniting the surrounding atmosphere. This is achieved through robust construction and specialized sealing techniques that ensure the fixture is airtight and resistant to the ingress of hazardous substances.
Explosion-proof lights are typically made from stainless steel, aluminum, and toughened glass, which can withstand harsh industrial conditions. These materials resist corrosion, impact, and extreme temperatures, ensuring the lights remain operational and safe in demanding environments.
Applications in High-Risk Areas
Explosion-proof lights are essential in industries such as oil refineries, chemical plants, and other settings where safety is paramount. They prevent the ignition of explosive materials, ensuring a safer work environment.
In oil refineries, explosion-proof lighting is used in areas where flammable gases and vapors are present. These lights provide reliable illumination for maintenance and operational tasks while minimizing the risk of igniting potentially explosive mixtures.
Chemical plants also require explosion-proof lighting to ensure safety in environments where volatile chemicals are handled. Proper lighting is crucial for detecting leaks, spills, and other hazards, allowing workers to respond quickly and effectively.
Other high-risk areas where explosion-proof lighting is used include mining operations, grain processing facilities, and paint manufacturing plants. In these environments, combustible dust and fumes necessitate using lighting fixtures that can withstand and contain potential ignition sources.
Color Temperature: Choosing the Right Light
Cool White vs. Warm White
Selecting the appropriate color temperature is vital for creating a conducive working environment.
Cool White Light (5000K-6500K): It enhances concentration and visibility, making it ideal for task-oriented areas such as manufacturing floors and inspection stations. The bright, crisp light helps reduce eye strain and improves focus, which can lead to increased productivity and fewer errors.
Warm White Light (2700K-3000K): Warm white light creates a comfortable and inviting atmosphere, making it suitable for break rooms, relaxation areas, and spaces where workers take breaks. The softer light helps create a relaxing environment, improving employee well-being and morale.
Impact on Productivity and Safety
The right color temperature can profoundly impact productivity and safety. Proper lighting design that considers both the functional and psychological aspects of light can significantly improve workplace performance.
Productivity: Adequate and appropriate lighting reduces eye strain and fatigue, allowing employees to work more efficiently and effectively. In areas where precision work is performed, such as assembly lines or quality control stations, the right lighting can enhance accuracy and reduce the likelihood of mistakes.
Safety: Proper lighting is essential for preventing accidents and injuries. Well-lit environments reduce the risk of trips, falls, and other hazards. In addition, good lighting can help workers quickly identify potential dangers, such as spills or equipment malfunctions, enabling them to take prompt action.
Human-Centric Lighting (HCL)
What is HCL?
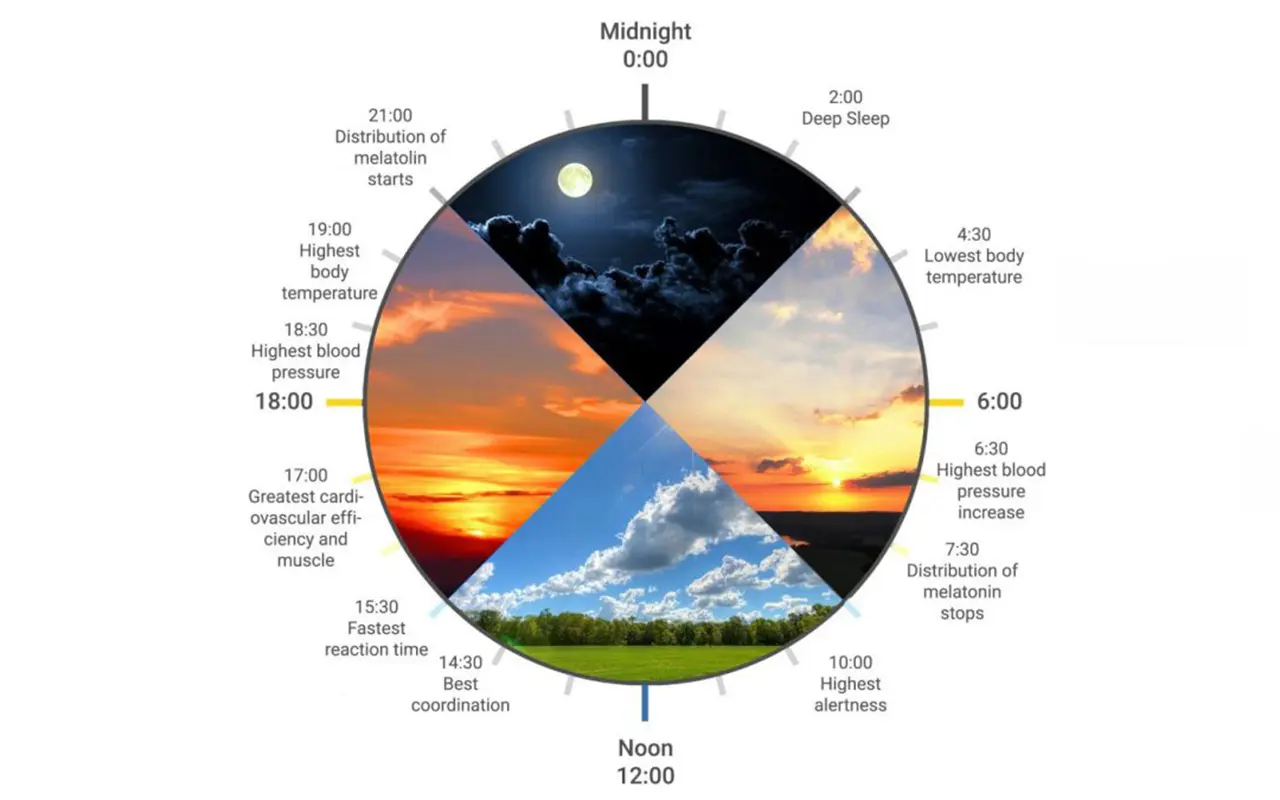
Human-centric lighting (HCL) is designed to mimic natural daylight patterns, supporting workers’ circadian rhythms and overall well-being. HCL systems adjust color temperature and brightness throughout the day to align with natural light cycles.
Dynamic Lighting: HCL systems use tunable white LED technology to change the color temperature and intensity of light. In the morning, cooler, brighter light can enhance alertness and productivity, while warmer, softer light in the evening can promote relaxation and prepare the body for rest.
Biological Benefits: Exposure to appropriate lighting at the right times of day can help regulate sleep-wake cycles, improve mood, and boost overall health. This is particularly beneficial in industrial settings where workers may have limited access to natural light.
Advantages for Industrial Workers
Implementing HCL in industrial environments offers several advantages for workers, including improved comfort, productivity, and health.
Comfort: HCL systems create a more pleasant and comfortable working environment by providing lighting that mimics natural daylight. Workers experience less eye strain and fatigue, which can enhance their overall job satisfaction.
Productivity: Proper lighting can improve concentration and performance. Studies have shown that workers in well-lit environments are more alert and can perform tasks more accurately. HCL systems can boost productivity by ensuring workers have the right lighting conditions for daily tasks.
Health: HCL systems support the circadian rhythms, which can lead to better sleep patterns and overall health. Workers who experience regular, natural light cycles are less likely to suffer from issues like insomnia and depression, which can improve their long-term well-being and reduce absenteeism.
CRI: Importance in Industrial Work
CRI measures a light source’s ability to reveal the true colors of objects. A higher CRI (80+) ensures accurate color representation, which is crucial in tasks requiring color differentiation.
The Color Rendering Index (CRI) measures a light source’s ability to reveal the true colors of objects compared to natural light. A higher CRI indicates better color accuracy, which is crucial in tasks that require precise color differentiation.
Visual Clarity: High CRI lighting ensures that colors appear more vibrant and true to life, which can improve the accuracy of tasks such as painting, assembling, and inspecting products. This is essential in quality control processes, where distinguishing between subtle color variations can be critical.
Task Accuracy: In environments where detailed work is performed, such as electronics assembly or medical device manufacturing, high CRI lighting helps workers see fine details more clearly. This reduces the risk of errors and enhances overall product quality.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Lighting
Energy-efficient lighting solutions, like LEDs, reduce energy consumption and lower operational costs. They also contribute to environmental sustainability by decreasing the facility’s carbon footprint.
Cost Savings: Energy-efficient lights reduce electricity bills and cooling costs by consuming less power and generating less heat. LEDs, in particular, offer significant savings over their lifespan, which can offset the higher initial investment.
Environmental Impact: Energy-efficient lighting reduces greenhouse gas emissions and decreases the demand for fossil fuels. Businesses can demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship and corporate social responsibility by choosing sustainable lighting options.
Strategies to Reduce Energy Costs
Implementing smart lighting controls, using motion sensors, and optimizing natural light can significantly reduce energy costs. Retrofitting existing systems with energy-efficient fixtures also offers substantial savings.
Smart Lighting Controls: Automated systems that adjust lighting levels based on occupancy and natural light availability can optimize energy use. For example, installing daylight sensors that dim or turn off lights when sufficient natural light is present can save energy.
Motion Sensors: In areas with sporadic occupancies, such as storage rooms or restrooms, motion-activated lighting ensures that lights are only on when needed. This reduces energy waste and extends the lifespan of the fixtures.
Retrofitting: Upgrading outdated lighting systems with modern, energy-efficient alternatives can yield immediate savings. Retrofitting projects often include replacing incandescent or fluorescent bulbs with LEDs, which consume less power and last longer.
Choosing Durable Lighting Fixtures
Industrial environments require robust lighting fixtures that withstand dust, debris, and harsh conditions. Durable lights reduce maintenance needs and enhance operational reliability.
Robust Construction: Fixtures made from high-quality materials, such as stainless steel or aluminum, are more resistant to corrosion and damage. Sealed housings that protect against dust and moisture ingress are essential in environments like manufacturing plants and warehouses.
Impact Resistance: Impact-resistant lighting fixtures are crucial in facilities where equipment and materials are frequently moved, such as loading docks and production lines. These lights can withstand accidental bumps and collisions, ensuring continuous operation.
Technological Advancements in Industrial Lighting
Technological advancements have significantly transformed industrial lighting, making it more efficient, adaptive, and sustainable. Modern lighting solutions improve visibility and safety and offer smart features that enhance operational efficiency and reduce energy consumption. Here, we delve into some of the most impactful advancements in industrial lighting technology.
Integration with IoT
Integrating smart lighting systems with the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized how industrial lighting is managed and controlled. IoT-enabled lighting systems provide real-time monitoring and control, allowing facility managers to optimize lighting based on various environmental factors.
IoT-Enabled Features: These systems can adjust lighting levels based on occupancy, daylight availability, and specific operational needs. Sensors detect movement and automatically turn lights on or off, ensuring energy is not wasted in unoccupied areas. Daylight sensors adjust artificial lighting to complement natural light, maintaining optimal illumination levels throughout the day.
Data Analytics: IoT-enabled lighting systems collect data on usage patterns, energy consumption, and system performance. This data can be analyzed to identify inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement, leading to better energy management and cost savings.
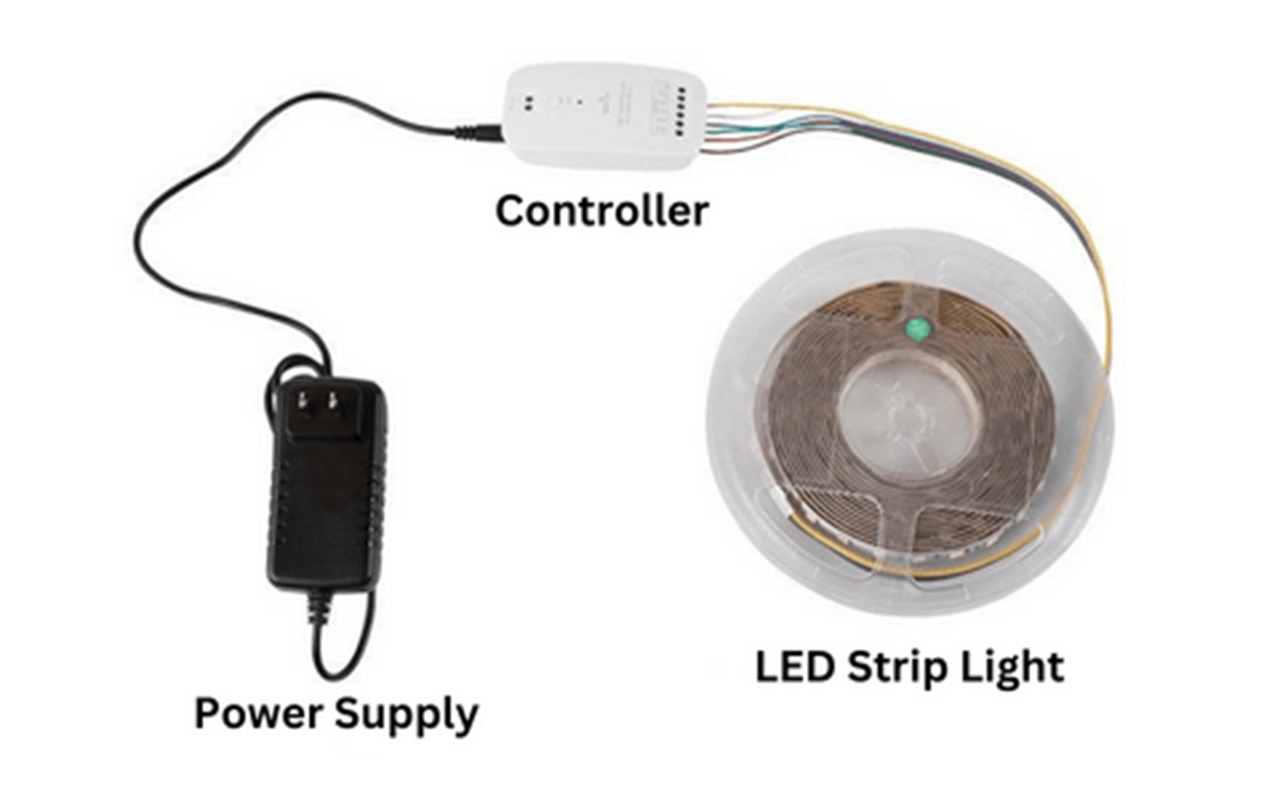
Wireless Control and Automation
Wireless lighting systems offer significant benefits in terms of installation and operation, making them ideal for dynamic and evolving industrial environments.
Ease of Installation: Wireless systems eliminate the need for extensive wiring, reducing installation time and costs. This is particularly advantageous in retrofitting projects or facilities where flexibility and adaptability are crucial.
Scalability: Wireless lighting systems can be easily expanded or reconfigured to meet changing needs. New fixtures can be added without major disruptions, and the system can be adjusted to accommodate different layouts and operational requirements.
Control and Monitoring: Wireless systems provide centralized control, allowing facility managers to adjust lighting settings and monitor performance from a single interface. This enhances operational efficiency and simplifies management tasks.
FAQ
Q: How many Lux should industrial lighting provide for optimal productivity?
A: The optimal Lux level for industrial lighting varies based on the specific tasks and areas. For general warehouse lighting, 150-300 Lux is typically sufficient. In areas requiring detailed work, such as assembly lines or inspection stations, higher illumination levels of 500-700 Lux are recommended to ensure accuracy and reduce eye strain.
Q: What are the benefits of using LED lighting in industrial settings?
A: LED lighting offers several benefits in industrial environments, including significant energy savings, reduced maintenance costs, and improved light quality. LEDs consume up to 75% less energy than traditional lighting options and have a longer lifespan, which reduces the frequency of replacements. They also provide bright, consistent illumination with better color rendering, enhancing visibility and safety.
Q: How does color temperature affect industrial lighting?
A: Color temperature impacts both productivity and comfort in industrial settings. Cool white light (5000K-6500K) is ideal for task-oriented areas as it enhances concentration and visibility. Warm white light (2700K-3000K) creates a more relaxing environment, suitable for break rooms and areas where workers need to unwind. The right color temperature helps reduce eye strain and improves overall work efficiency.
Q: What is Human-Centric Lighting (HCL), and how does it benefit industrial workers?
A: Human-centric lighting (HCL) mimics natural daylight patterns to support workers’ circadian rhythms and well-being. HCL systems adjust color temperature and brightness throughout the day, enhancing alertness in the morning with cooler light and promoting relaxation in the evening with warmer light. This lighting approach improves comfort, productivity, and overall health, reducing fatigue and enhancing workplace performance.
Q: How can smart lighting systems improve energy efficiency in industrial facilities?
A: Smart lighting systems integrate with IoT to provide real-time monitoring and control, adjusting lighting based on occupancy, daylight availability, and other environmental factors. These systems can automatically dim or turn off lights in unoccupied areas and optimize lighting levels throughout the day, leading to substantial energy savings and lower operational costs. They also enable remote monitoring and management, simplifying maintenance tasks.
Q: Why is CRI (Color Rendering Index) important in industrial lighting?
A: CRI measures a light source’s ability to reveal objects’ true colors accurately. A high CRI (80+) is crucial in industrial settings where precise color differentiation is required, such as manufacturing and quality control. High CRI lighting enhances visual clarity, improves task accuracy, and reduces errors, improving overall product quality and efficiency.
Q: What are the key considerations when choosing durable lighting fixtures for industrial environments?
A: When selecting lighting fixtures for industrial settings, it’s essential to choose durable options that can withstand dust, debris, and harsh conditions. Look for fixtures made from robust materials like stainless steel or aluminum and those with sealed housings to protect against dust and moisture. Impact-resistant fixtures are also important in environments with frequent equipment and material movement, ensuring continuous operation and reducing maintenance needs.
Q: How can wireless lighting controls benefit industrial operations?
A: Wireless lighting controls offer flexibility and ease of installation, making them ideal for dynamic industrial environments. These systems can be easily configured and reconfigured without extensive wiring, allowing quick adjustments to meet changing needs. Wireless controls enable centralized management, allowing facility managers to monitor and adjust lighting settings remotely, enhancing operational efficiency and simplifying maintenance tasks.
Conclusion
In summary, industrial lighting is critical to a safe, productive, and efficient workspace. By understanding the different types of lighting and key design considerations, you can make informed decisions that enhance your facility’s operations. Selecting the right industrial lighting requires a comprehensive approach that considers the unique needs of your facility. Prioritize energy efficiency, safety, and sustainability to create a well-lit environment that supports your business goals. For personalized advice and professional lighting solutions, consult with experienced lighting providers.
As you look to upgrade your lighting systems, consider partnering with Unitop, one of China’s leading manufacturers of LED strip lights and LED neon flex. Our expertise in the LED industry ensures that you receive top-quality products designed for durability and performance. If you have further questions or specific requirements, please contact us immediately. Let us help you illuminate your path to success with our innovative lighting solutions.

Tom is now the Sales Manager of Unitop (China) Co., Limited. He has been in the LED Lighting industry ever since 2005. He is an expert in sales & marketing, and factory management. He likes bodybuilding, and he is also a crazy Apple Fan! He is a hard-working guy and loves to learn and try new things.
Email: tom@unitopledstrip.com WhatsApp: +86-18680307140










Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!