Emergency lighting is not just an add-on; it’s a critical component of building safety that can make the difference between chaos and calm during an emergency. Imagine being in a shopping mall or a high-rise office when the power suddenly cuts out. Without emergency lighting, finding your way to safety would be daunting and dangerous. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of emergency lighting, highlighting its importance, various types, and practical applications to ensure you’re prepared for any unexpected situation.
Understanding why you need emergency lighting is crucial. Safety and compliance are the primary reasons, as these systems significantly enhance public safety by providing clear, illuminated paths for evacuation. Beyond safety, emergency lighting is a legal requirement in many regions, ensuring that buildings meet stringent regulations to protect occupants. The benefits are manifold, from reducing panic during emergencies to ensuring operational continuity in critical facilities like hospitals.
Ready to enhance your understanding of emergency lighting and ensure the safety of your occupants? Let’s dive right in and explore everything you need to know about emergency lighting, from installation and maintenance to the latest innovations and regulatory requirements.
What is Emergency Lighting?
Emergency lighting is a crucial safety feature in buildings, designed to activate automatically during power outages or other emergencies. These lighting systems ensure that occupants can find their way to safety, reducing the risk of accidents and facilitating quick evacuations. Emergency lighting systems are indispensable in large public buildings such as malls, cinemas, and hotels, providing both ambient illumination for general visibility and specific lighting for exit signs and critical areas.
Emergency lighting comprises various components, including emergency escape, standby, and exit signage. Each of these elements serves a unique purpose, ensuring comprehensive coverage during emergencies. For example, emergency escape lighting guides occupants to the nearest exits, while standby lighting allows for the continuation of essential operations in critical facilities like hospitals and data centers. Properly lit exit signs are strategically placed to clearly indicate safe evacuation routes.
By maintaining visibility in hallways, stairwells, and other crucial points, emergency lighting helps prevent panic and injuries. It’s essential for high-occupancy buildings, where the potential for chaos during an emergency is higher. Moreover, the implementation of such systems is often mandated by building codes and regulations, making it a legal requirement as well as a safety measure.
Why Do You Need Emergency Lighting?
Safety is the foremost reason for installing emergency lighting. In the event of a power outage, fire, or other emergency, these systems provide the necessary illumination for safe evacuation. By ensuring that exits and escape routes are visible, emergency lighting significantly reduces the risk of injuries and fatalities.
Compliance with legal standards is another critical aspect. Various regulations mandate the installation of emergency lighting in public and commercial buildings. These laws are in place to ensure that all buildings are equipped to handle emergencies effectively, safeguarding the well-being of occupants. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, legal action, and even the closure of businesses until the standards are met.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) provide guidelines for emergency lighting in workplaces. These standards ensure that exit routes are adequately illuminated, and exit signs are clearly visible. In the United Kingdom, the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 and the Building Regulations 2010 set out similar requirements, emphasizing the importance of emergency lighting in ensuring public safety.
Benefits of Emergency Lighting Systems
The benefits of emergency lighting systems extend beyond mere compliance. These systems enhance overall building safety, providing peace of mind to occupants and building owners alike. Here are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Safety: By illuminating escape routes, staircases, and exits, emergency lighting helps prevent accidents during evacuations. It also ensures that safety equipment like fire extinguishers and first aid kits are easily located.
- Reduced Panic: In an emergency, clear visibility can reduce panic and confusion among occupants. Well-lit escape routes and exit signs guide people to safety in a calm and orderly manner.
- Operational Continuity: In facilities like hospitals and data centers, standby lighting ensures that critical operations can continue even during power outages. This is essential for patient care and data security.
- Legal Protection: By complying with regulations, building owners can avoid legal repercussions and potential shutdowns. Properly installed and maintained emergency lighting systems demonstrate a commitment to safety, which can be reassuring for both employees and customers.
- Insurance Benefits: Many insurance companies offer reduced premiums for buildings with robust safety systems, including emergency lighting. This can result in significant cost savings over time.
Overall, emergency lighting is a vital component of modern building safety, offering numerous benefits that extend beyond legal compliance.
Types of Emergency Lighting
Self-contained emergency lighting systems, also known as single-point systems, are designed with all necessary components housed within the light fixture itself. This includes the battery, lamp, and control unit. These systems are advantageous due to their simplicity and ease of installation, as they do not require extensive wiring.
Advantages of Self-Contained Systems:
- Ease of Installation: Self-contained systems are straightforward to install, making them ideal for smaller buildings or locations where wiring is impractical.
- Independent Operation: Each unit operates independently, ensuring that a failure in one does not affect the others.
- Flexibility: These systems are easily adaptable and can be installed in various locations without the need for significant infrastructure changes.
Disadvantages:
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to ensure each unit’s battery is fully charged and operational. This can be labor-intensive in large installations.
- Battery Life: Batteries in self-contained units typically need replacement every three to five years, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Central Battery Systems
Central battery systems utilize a single central power source to supply multiple light fixtures through fireproof wiring. These systems are commonly used in larger buildings where centralized control and maintenance are more efficient.
Advantages of Central Battery Systems:
- Centralized Maintenance: Maintenance is simplified as the batteries are housed in a central location, making it easier to monitor and service them.
- Cost-Effective: For large installations, central battery systems can be more cost-effective due to reduced wiring and maintenance costs.
- Reliability: These systems offer enhanced reliability, especially in critical infrastructure buildings like hospitals and banks.
Disadvantages:
- Complex Installation: The installation process is more complex and requires fire-resistant wiring, which can be costly.
- Space Requirements: A dedicated, well-ventilated compartment is needed for the battery storage area.
Monitoring Needs: Central battery systems require continuous monitoring and sub-circuit protection devices.
Comparison and Benefits
| Functie | Self-Contained Systems | Central Battery Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Installatie | Easier, less wiring | Requires extensive wiring |
| Onderhoud | Requires regular battery checks | Easier centralized maintenance |
| Kosten | Higher initial cost for units | Cost-effective for large installations |
| Reliability | Each unit operates independently | Centralized control, more reliable |
Both systems play a crucial role in ensuring safety during emergencies, and the decision should be based on a thorough assessment of the building’s specific requirements and resources.
Emergency Lighting Installation Locations
High-Risk Task Areas
High-risk task areas, such as chemical laboratories, heavy machinery zones, and power plants, require specialized emergency lighting. These areas need brighter illumination to ensure workers can safely perform shutdown procedures before evacuating. Proper lighting in these zones is crucial to avoid accidents that could lead to more severe disasters.
Escape Routes
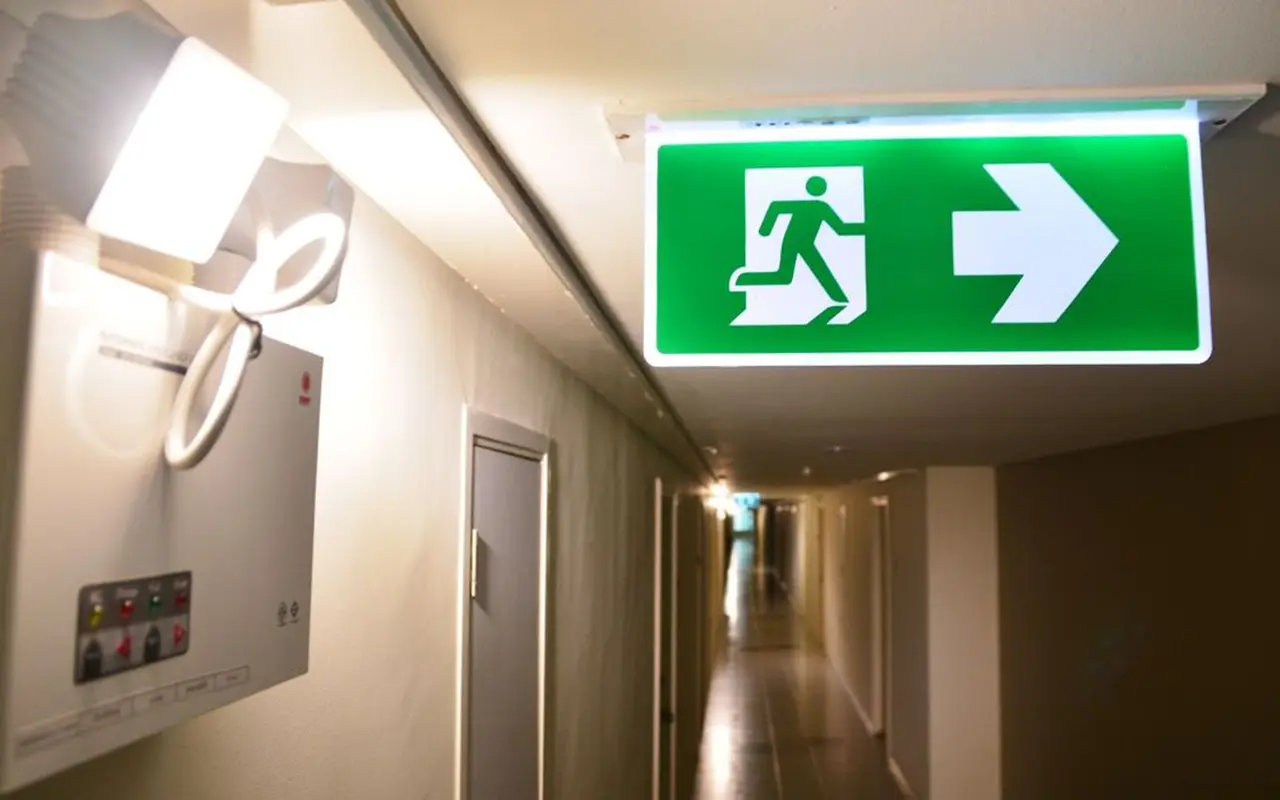
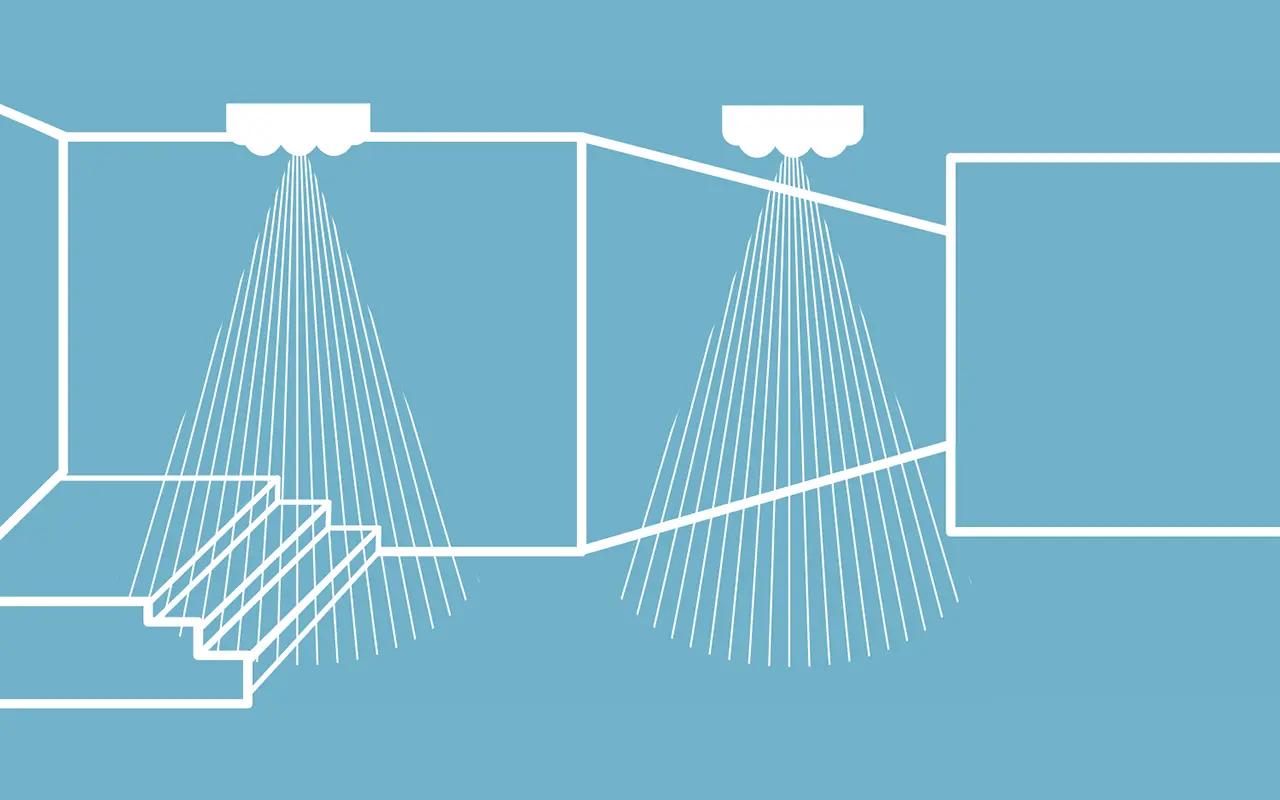
Escape routes are the primary paths used during an evacuation. These include corridors, staircases, and exits. Proper illumination along these routes is essential to guide occupants safely out of the building. Emergency lights should be placed at regular intervals and at critical points such as intersections and changes in direction to ensure continuous visibility.
Open Areas (Anti-Panic Areas)
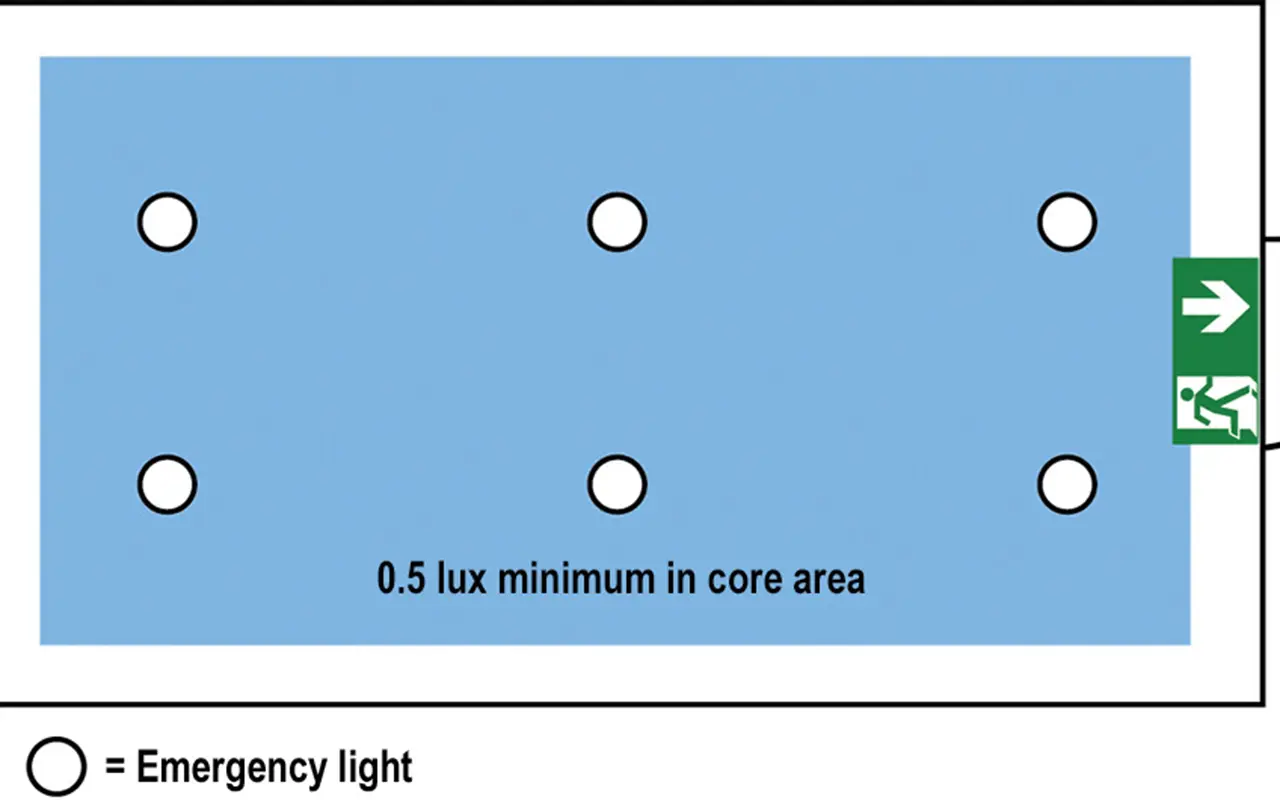
Open areas larger than 60 square meters, or smaller areas with high occupancy or specific hazards, require anti-panic emergency lighting. These lights help prevent panic by providing adequate illumination, allowing occupants to move safely and calmly toward escape routes. Proper lighting in these areas also aids in the identification of obstacles and hazards.
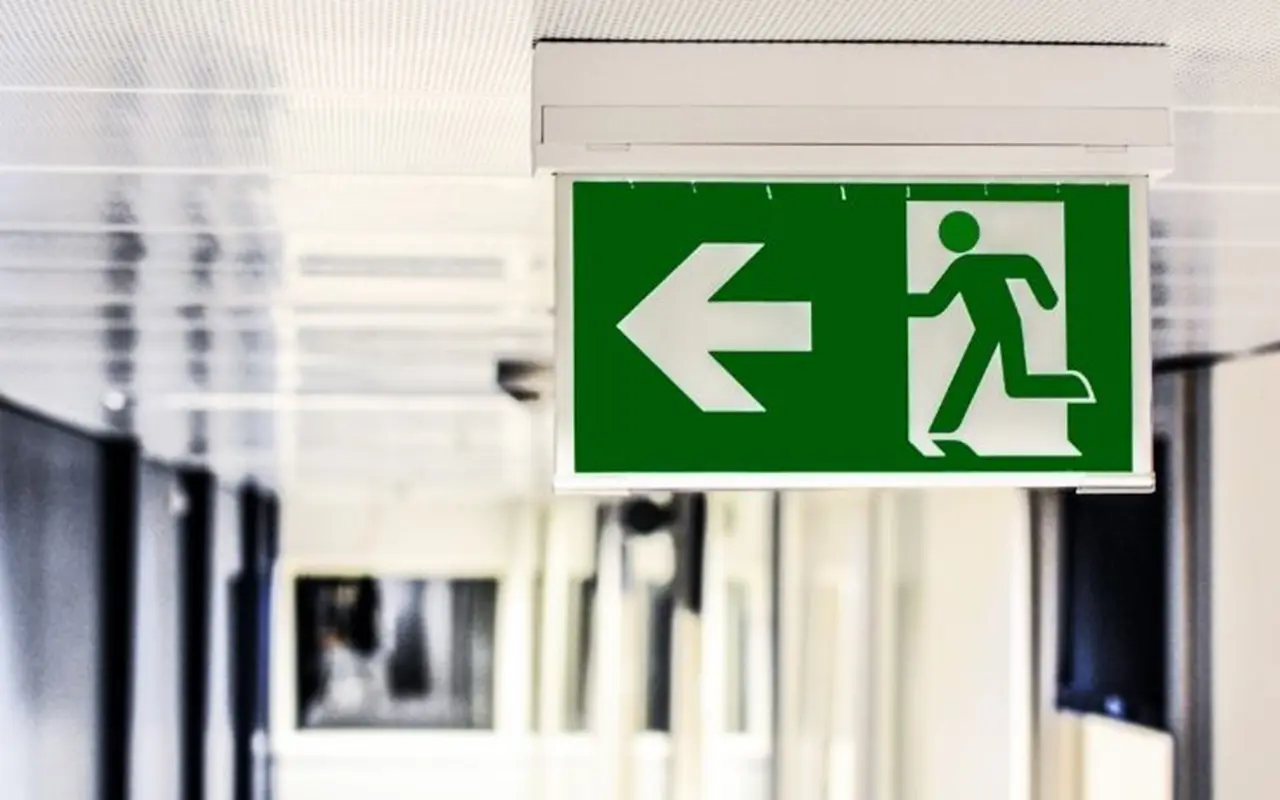
Exit Signs and Directional Lights
Exit signs and directional lights are critical for clearly marking evacuation paths. These signs should be strategically placed at every exit, intersection, and significant directional change. Properly illuminated exit signs ensure that occupants can easily find the nearest exits, even in smoky or dark conditions.
Emergency Lighting Design
Consultation & Risk Assessment
The design of an emergency lighting system begins with thorough consultation and risk assessment. This process involves collaboration between building owners, developers, architects, safety professionals, and enforcing authorities. The goal is to identify the building’s specific needs and risks to create an effective emergency lighting plan.
Key Considerations:
- Building Usage: Understanding how different areas of the building are used helps determine the appropriate lighting requirements.
- Occupancy Levels: Assessing the number of occupants at any given time ensures that the lighting design can handle the building’s capacity.
- Escape Routes: Identifying and marking escape routes is crucial for planning the placement of emergency lights.
H3 Placement and Coverage - Proper placement and coverage of emergency lighting ensure that all critical areas are illuminated. This includes exits, staircases, high-risk zones, and open areas. The design should ensure no part of the evacuation route is left in darkness, facilitating safe and efficient evacuations.
Required Light (Lux) Levels
The required brightness levels for emergency lighting vary depending on the location and use of the area. These levels are measured in lux, with different standards for different areas:
| Location | Minimum Lux Level |
|---|---|
| Large Open Areas | 0.5 lux |
| Exit Routes | 1 lux |
| High-Risk Task Areas | 15 lux |
| Exit Signs | 54 lux |
Duration and Performance
Emergency lights must provide illumination for at least three hours following a power failure. This duration covers most evacuation scenarios and ensures that the lighting remains functional until occupants have safely exited the building. The lights should also meet the required brightness levels (lux) to ensure visibility.
Aesthetic Considerations
While functionality is paramount, aesthetic considerations are also important. Emergency lighting systems should blend seamlessly with the building’s interior design. This ensures that the lights do not detract from the building’s aesthetic appeal while still providing essential safety features.
Regulations for Emergency Lighting
United States Regulations
In the United States, emergency lighting regulations are primarily governed by OSHA and ANSI standards. These regulations mandate adequate illumination for exit routes, clear marking of exits, and regular maintenance of emergency lighting systems. Compliance with these standards ensures that buildings are prepared for emergencies and that occupants can evacuate safely.
United Kingdom Regulations
The United Kingdom has stringent regulations for emergency lighting under the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 and the Building Regulations 2010 Fire Safety. These regulations require all public buildings to have adequate emergency lighting, comply with BS 5266-1 for escape routes, and ensure that all safety signs are illuminated.
Other International Standards
Different countries adhere to various standards, such as the EN 1838 standard in Europe, which outlines the requirements for emergency lighting and its testing. These international standards ensure a consistent approach to emergency lighting, enhancing safety across different regions.
Installation and Maintenance
Installation Best Practices
Installing emergency lighting should follow best practices, ensuring all components are correctly placed and wired. Using fire-resistant materials and ensuring compliance with local regulations are crucial steps. Proper installation not only guarantees the system’s effectiveness but also ensures the safety of the building’s occupants.
Regular Testing and Maintenance
Regular testing and maintenance are essential to ensure the system functions correctly during an emergency. These procedures help identify and address any issues before they can compromise the system’s effectiveness.
- Monthly Tests
Monthly tests involve checking the functionality of all emergency lights and batteries, ensuring they switch on when needed. This includes inspecting indicators, control units, and batteries to ensure they are in good working condition. - Annual Tests
Annual tests require a more thorough inspection, including running the lights on battery power for the full duration to ensure reliability. These tests verify that the system can provide the required illumination for the specified period and that all components are functioning correctly.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Common issues with emergency lighting include battery failures, faulty wiring, and light fixture problems. Regular inspections and prompt troubleshooting are vital to maintaining the system’s effectiveness. Addressing issues promptly ensures that the emergency lighting system is always ready to perform when needed.
Innovations and Future Trends
Advances in LED Technology
LED technology has revolutionized emergency lighting, offering energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and improved brightness. LED emergency lights are more reliable and require less maintenance than traditional options. Their ability to provide consistent illumination while consuming less power makes them an ideal choice for modern emergency lighting systems.
Smart Emergency Lighting Systems
Smart emergency lighting systems integrate with building management systems, offering remote monitoring and control. These systems can automatically test themselves and report any issues, ensuring constant readiness. Smart systems also allow for real-time adjustments, optimizing the lighting based on current conditions and needs.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Modern emergency lighting systems focus on sustainability, using energy-efficient LEDs and eco-friendly materials. These systems not only reduce energy consumption but also have a lower environmental impact. By incorporating sustainable practices, building owners can contribute to environmental conservation while ensuring the safety of their occupants.
FAQ's
Q: Why are LED strip lights an essential component of emergency lighting systems?
A: LED strip lights are essential in emergency lighting systems due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and reliability. They provide consistent illumination during power outages, ensuring that escape routes and critical areas are well-lit for safe evacuations.
Q: What are the benefits of using LED technology in emergency lighting?
A: LED technology in emergency lighting offers numerous benefits, including lower energy consumption, longer lifespan, and improved brightness. LEDs require less maintenance and provide reliable performance, making them ideal for safety-critical applications.
Q: How does emergency lighting enhance safety during power outages?
A: Emergency lighting enhances safety by providing clear, illuminated paths for evacuation, reducing the risk of accidents and panic. It ensures that occupants can find their way to exits and safety equipment even in the dark.
Q: What is the difference between self-contained and central battery emergency lighting systems?
A: Self-contained systems house all components within the fixture, making them easier to install but requiring more maintenance. Central battery systems use a single power source to supply multiple fixtures, offering easier centralized maintenance but requiring more complex installation.
Q: How often should emergency lighting systems be tested and maintained?
A: Emergency lighting systems should be tested monthly for functionality and annually for a thorough inspection, including running lights on battery power for the full duration. Regular maintenance ensures the system remains operational during emergencies.
Q: What are the key regulations for emergency lighting in the United States?
A: In the United States, emergency lighting regulations are primarily governed by OSHA and ANSI standards. These regulations mandate adequate illumination for exit routes, clear marking of exits, and regular maintenance to ensure compliance and safety.
Q: Why is it important to have emergency lighting in high-risk task areas?
A: High-risk task areas, such as chemical labs and heavy machinery zones, require brighter emergency lighting to ensure workers can safely perform shutdown procedures before evacuating. Proper lighting in these zones helps prevent accidents that could lead to more severe disasters.
Q: How does smart emergency lighting improve building safety?
A: Smart emergency lighting integrates with building management systems, offering remote monitoring and control. These systems can automatically test themselves and report issues, ensuring constant readiness and optimizing lighting based on current conditions.
Q: What are the required light levels for different areas in emergency lighting?
A: The required light levels vary depending on the area. For example, exit routes should have a minimum of 1 lux, large open areas 0.5 lux, high-risk task areas 15 lux, and exit signs 54 lux. Meeting these standards ensures adequate visibility for safe evacuations.
Q: How can I ensure my emergency lighting system is compliant with international standards?
A: To ensure compliance with international standards, such as EN 1838 in Europe, consult with an emergency lighting expert during the design and installation phases. Regular testing and maintenance according to these standards are crucial for ongoing compliance and safety.
Conclusie
Emergency lighting is a vital part of building safety, providing essential illumination during power failures and emergencies. Understanding the types, installation requirements, and regulations ensures that buildings are well-equipped to handle any situation. By staying updated with the latest technologies and standards, building owners can ensure the safety and security of their occupants. Investing in reliable emergency lighting is not just a legal obligation but a commitment to safety and peace of mind.
As you consider the best solutions for your needs, remember that Unitop is one of China’s leading manufacturers of LED-strip verlichting en LED neon flex, renowned for our high-quality products and expertise in the LED industry. If you have any further questions or specific requirements, don’t hesitate to contact met ons opnemen. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in ensuring the safety and efficiency of your lighting systems. Trust Unitop to illuminate your path to safety and excellence.

Tom is nu de Sales Manager van Unitop (China) Co.. Hij is in de LED Verlichting industrie sinds 2005. Hij is een expert in verkoop & marketing, en fabrieksmanagement. Hij houdt van bodybuilding, en hij is ook een gekke Apple-fan! Hij is een hardwerkende man en houdt ervan te leren en nieuwe dingen te proberen.
Email: tom@unitopledstrip.com WhatsApp: +86-18680307140









Laat een reactie achter
Wil je meedoen aan de discussie?Voel je vrij om bij te dragen!