Do you find yourself battling headaches and wondering if your LED strip lights could be the culprit? Our guide delves into the science behind LED lighting and its potential impacts on your health.
LED strip lights may contribute to headaches through flickering, excessive brightness, and blue light exposure, potentially triggering discomfort in sensitive individuals.
Keep reading to uncover how LED lighting can affect your health and learn practical tips to minimize risks and enhance your indoor lighting experience.
Understanding How LED Strip Lights Might Trigger Headaches
LED strip lights are not just popular for their sleek appearance and versatility; they’re celebrated for their energy efficiency and the dynamic control they offer over home and office lighting. However, their widespread adoption brings to light some less-discussed downsides, particularly their potential to induce headaches in sensitive individuals.
- Flicker Sensitivity: One of the primary headache-inducing factors of LED lights is their flicker rate. While traditional incandescent bulbs emit a steady glow, LED lights flicker at a rapid rate — a phenomenon often imperceptible to the human eye. This flickering can cause a rapid contraction and relaxation of the eye muscles, leading to eyestrain and subsequent headaches. For those sensitive to light, even a minor flicker can trigger severe discomfort.
- Brightness and Contrast: The intensity of light emitted by LED strips can also be a contributing factor. LEDs are capable of emitting a very high level of brightness compared to traditional lighting solutions. When used in dimly lit environments, the stark contrast between the LED brightness and the surrounding darkness can strain the eyes. This is particularly problematic in settings like home offices or bedrooms, where excessive brightness can lead to prolonged eye strain and headaches.
- Blue Light Exposure: LEDs emit a significant amount of blue light, which has been shown to disrupt melatonin production and alter sleep patterns. Beyond affecting sleep, exposure to blue light has been linked directly to increased eyestrain and headaches. The disruption of natural sleep cycles alone can be a trigger for headaches and migraines, making prolonged exposure to LED lighting a concern for nighttime users or those who spend substantial time in artificially lit environments.
The Role of Color Temperature in LED Headaches
The impact of LED lights on headaches can also vary dramatically based on the color temperature of the light emitted. Color temperature is a key factor in determining how ‘harsh’ or ‘soft’ a light feels to our eyes, and it plays a crucial role in user comfort.
- Cool vs. Warm Light: LED lights are available in a spectrum of color temperatures. Cooler lights, which have a blueish hue, are known to be more energizing but can also be more likely to induce headaches due to their high energy output. On the other hand, warm lights, which emit a yellowish hue, tend to be less stimulating and are often perceived as more comforting to the eyes. Selecting the right color temperature for different settings can greatly reduce the risk of headaches, especially in environments where individuals are exposed to light for prolonged periods.
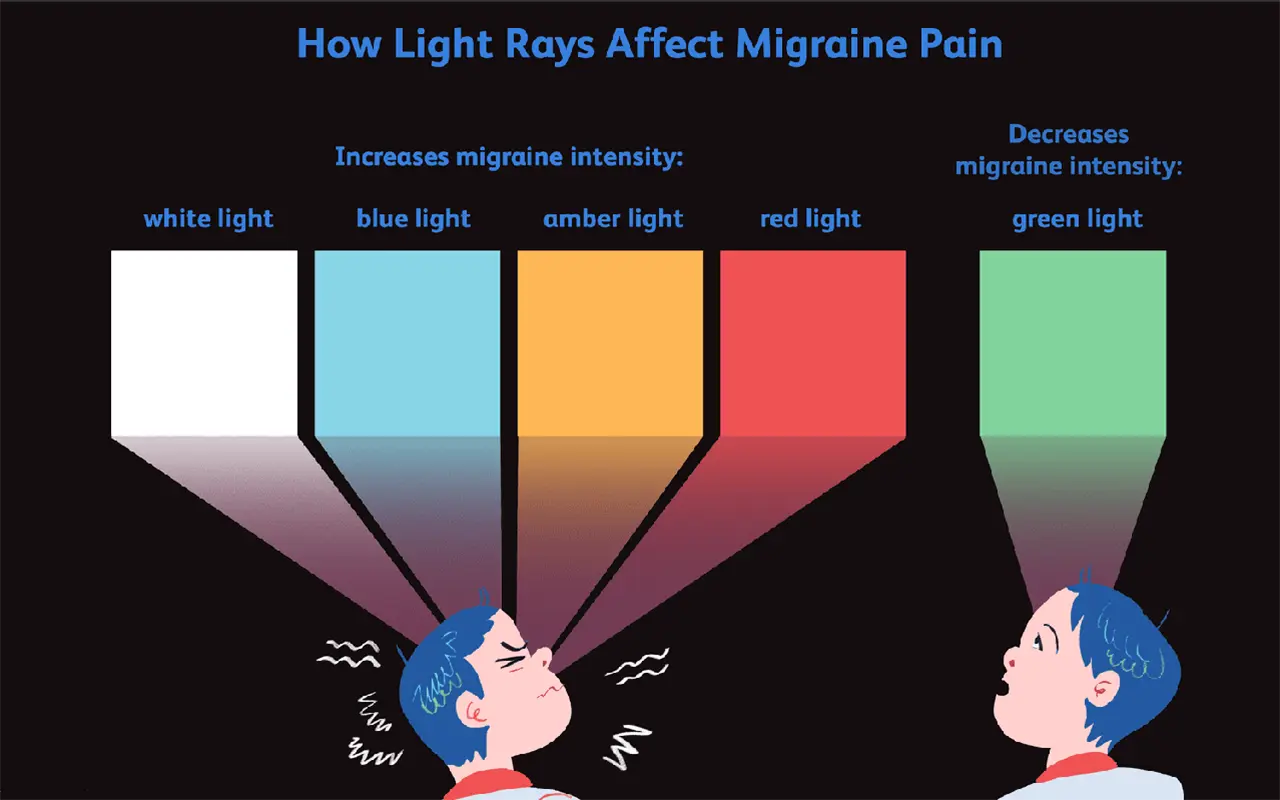
- Green Light and Migraines: Interestingly, specific research into the effects of different light colors on migraines has highlighted green light as potentially beneficial. Studies suggest that green LED light tends to produce less strain and can actually reduce the frequency of migraine attacks. This effect is thought to be due to green light’s ability to minimize retinal stress, thereby producing a soothing effect on the brain. For those particularly sensitive to migraines, substituting standard LEDs with green-tinted options could be an effective mitigation strategy.
Symptoms Indicative of LED-Induced Headaches
When it comes to the effects of LED lighting, the symptoms can vary widely, but recognizing them early can be key to preventing and managing discomfort. LED-induced headaches and related symptoms often manifest subtly before developing into more persistent conditions.
- Common Symptoms: The most immediate symptoms associated with LED exposure include persistent headaches and migraines that develop during or after exposure to LED lighting. Visual disturbances are also common; this might include blurred vision which can occur after long periods of exposure to bright LED lights, or when transitioning from a brightly lit environment to a darker one. Eye discomfort, characterized by a burning sensation or irritation in the eyes, can also indicate that the lighting conditions are less than ideal.
- Severe Cases: In more severe cases, individuals may experience heightened photosensitivity—this is particularly noticeable in environments where LED lights flicker beyond the perceptible rate for most people but are still detectable by those with sensitive vision. This sensitivity can exacerbate conditions like migraine or epilepsy, where light sensitivity is a known trigger. Extended exposure under such conditions can lead to debilitating episodes, severely affecting one’s quality of life.
Who is Most at Risk from LED Headaches?
Understanding who is most at risk from LED-induced headaches can help in developing strategies to mitigate these risks. Some individuals may be more prone to symptoms due to inherent conditions or environmental factors.
- Existing Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, or chronic eye disorders like dry eye syndrome are particularly vulnerable. For these people, the flicker and blue light emitted by LED strips can trigger more frequent and intense episodes. Migraine sufferers, for example, often report that certain types of artificial lighting can bring on an attack, necessitating careful management of their exposure to LEDs.
- Environmental Factors: The design of the lighting environment can also play a significant role in the onset of headaches. People working in poorly lit areas, where LED lights are the primary source of illumination, may experience more strain. Similarly, environments where lights are improperly positioned, resulting in direct exposure or significant glare, can increase the risk of headaches. This is often seen in offices or industrial settings where overhead LED lighting is predominant and not tailored to the needs of individual workstations.
For those who find themselves frequently battling with symptoms of LED-induced discomfort, understanding these risk factors is the first step toward mitigating their impact. Adjustments in lighting quality, positioning, and even the type of LEDs used can make substantial differences in comfort and health.
Proactive Measures to Prevent Headaches from LED Lights
To effectively minimize the risk of headaches from LED lighting, it’s essential to take proactive steps in choosing and setting up your lighting systems. Here’s how you can ensure a healthier lighting environment:
- Quality of Lights: Not all LED lights are created equal. Opting for high-quality, flicker-free LED options is crucial. These lights are designed to reduce the rapid flickering associated with cheaper models, which is often the cause of eyestrain and headaches. High-quality LEDs also tend to have better color consistency and more reliable output, which contributes to a more stable and comfortable lighting environment.
- Proper Installation: The way LED lights are installed can significantly affect their impact on your health. It is important to ensure that LEDs are installed in a way that minimizes glare and maximizes balanced light distribution. This might mean adjusting the placement of LED strips to avoid direct eye contact or using fixtures that diffuse light evenly. For workspaces, ensuring that lights are positioned to illuminate the desk without reflecting off screens can also help reduce glare.
- Use of Dimmers: Integrating dimmers with your LED lighting setup can provide significant benefits. Dimmers allow you to adjust the brightness of the lights according to the time of day and your specific activities, which helps in maintaining optimal lighting. This adaptability can be particularly helpful in reducing eye strain throughout the day, as you can lower lights to a comfortable level during high-focus tasks or in the evenings to prepare for bedtime.
Quando procurar ajuda profissional
While adjusting your lighting setup can alleviate many of the symptoms associated with LED-induced headaches, there are times when professional advice is necessary:
- Persistent Symptoms: If you have made all the recommended adjustments and still experience frequent headaches, migraines, or other related symptoms, it may be time to consult a healthcare professional. Persistent symptoms could indicate an underlying condition that might require medical intervention.
- Evaluating Eye Health: Regular eye check-ups can help rule out or manage eye health issues that might be exacerbated by LED lights. An optometrist can provide personalized advice on eyewear and lighting based on your specific vision needs.
- Special Conditions: For individuals with conditions like epilepsy, where flickering lights can trigger seizures, or chronic migraine sufferers who are sensitive to certain light spectrums, consulting with a specialist is crucial. These professionals can offer guidance on environmental adjustments and possibly prescribe medication or other treatments to manage sensitivity.
Understanding when to seek help is essential, as it not only addresses the symptoms but also aids in identifying any deeper health concerns. Proactively managing your environment and being aware of when symptoms are out of the ordinary can greatly improve your quality of life in the face of challenges posed by modern lighting technologies.
FAQs
Q: What makes LED strip lights a cause of headaches?
A: LED strip lights can cause headaches primarily due to their flicker sensitivity, high brightness, and the significant blue light they emit. These factors can trigger eyestrain, disrupt sleep patterns, and intensify headache symptoms, especially in individuals sensitive to light.
Q: Can the color temperature of LED lights influence headache frequency?
A: Yes, the color temperature of LED lights plays a crucial role in their impact on headaches. Cooler, blue-tinted LEDs are more likely to contribute to headache symptoms compared to warmer, yellow-tinted LEDs, which are generally softer on the eyes and less likely to cause discomfort.
Q: Are there specific symptoms that indicate LED strip lights are causing my headaches?
A: Symptoms that LED strip lights may be contributing to your headaches include persistent headaches or migraines, eye strain, visual disturbances like blurred vision, and increased sensitivity to light. If you experience these symptoms predominantly in environments lit by LEDs, the lights might be a contributing factor.
Q: Who is most at risk from headaches caused by LED lights?
A: Individuals with pre-existing conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, or chronic eye issues like dry eye syndrome are more susceptible to headaches caused by LED lights. Environmental factors like working in poorly lit areas or with high exposure to LED lights can also increase risk.
Q: How can I minimize the risk of headaches from LED lights?
A: To reduce the risk of headaches from LED lights, opt for high-quality, flicker-free LEDs, ensure proper installation to minimize glare, and use dimmers to adjust lighting intensity. This helps create a more comfortable environment that is less likely to trigger headaches.
Q: What are some effective alternatives to LED lighting if I’m sensitive?
A: For those sensitive to LED lighting, alternatives include incandescent bulbs, halogen bulbs, compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs), and utilizing natural light. Each of these options offers different benefits, such as reduced flicker or softer light, which can help alleviate light-induced headaches.
Q: When should I consider consulting a healthcare professional about my headaches?
A: If adjustments to your lighting environment don’t alleviate your symptoms, or if your headaches are frequent and severe, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable. They can help determine if there’s an underlying condition causing your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment.
Q: Why do my new LED strip lights flicker?
A: Flickering in new LED strip lights could be due to several factors including incompatible dimmer switches, poor quality LEDs, or incorrect installation. Ensuring compatibility between all components and using high-quality LEDs can help prevent flickering.
Q: Can flickering LED strip lights cause any harm?
A: While flickering LED lights are generally not harmful, they can cause eyestrain and headaches. Continuous flickering might also shorten the lifespan of the LEDs and indicate underlying electrical issues that might need attention.
Q: How do I choose the best-LED lighting option to avoid headaches?
A: When choosing LED lighting to avoid headaches, look for products labeled as flicker-free and those with adjustable color temperatures. Opt for warmer tones for general use and consider the installation environment to ensure that the lighting is evenly distributed without excessive glare.
Summary and Key Takeaways
This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive overview of how LED lighting, particularly LED strip lights, may contribute to headaches and what steps can be taken to prevent them. By understanding the characteristics of LED lights, recognizing symptoms, and knowing who might be more at risk, individuals can make informed decisions about their lighting choices. Additionally, practical tips for mitigating exposure and exploring alternatives can help improve one’s overall comfort and well-being in LED-lit environments.
In exploring the myriad lighting options suitable for those sensitive to LED lights, it’s crucial to choose products from a trusted leader in the industry. Unitop, one of China’s leading manufacturers of Fitas de LED e LED neon flex, stands out for its commitment to quality and innovation. Whether you’re seeking alternatives due to light sensitivity or simply looking for superior lighting solutions, Unitop offers a range of products designed to meet diverse needs with precision and reliability. If you have further questions or specific requirements, don’t hesitate to contacte-nos immediately. Trust Unitop to illuminate your space with expertise and care, ensuring your lighting choices are both comfortable and effective.
Publicações relacionadas

Tom é agora o Gerente de Vendas de Unitop (China) Co., Limited. Ele tem estado no Iluminação LED indústria desde 2005. Ele é um especialista em vendas & marketing, e gestão de fábricas. Ele gosta de musculação, e é também um fã louco da Apple! Ele é um tipo trabalhador e adora aprender e experimentar coisas novas.
Email: tom@unitopledstrip.com WhatsApp: +86-18680307140








Deixe uma resposta
Quer juntar-se à discussão?Esteja à vontade para contribuir!